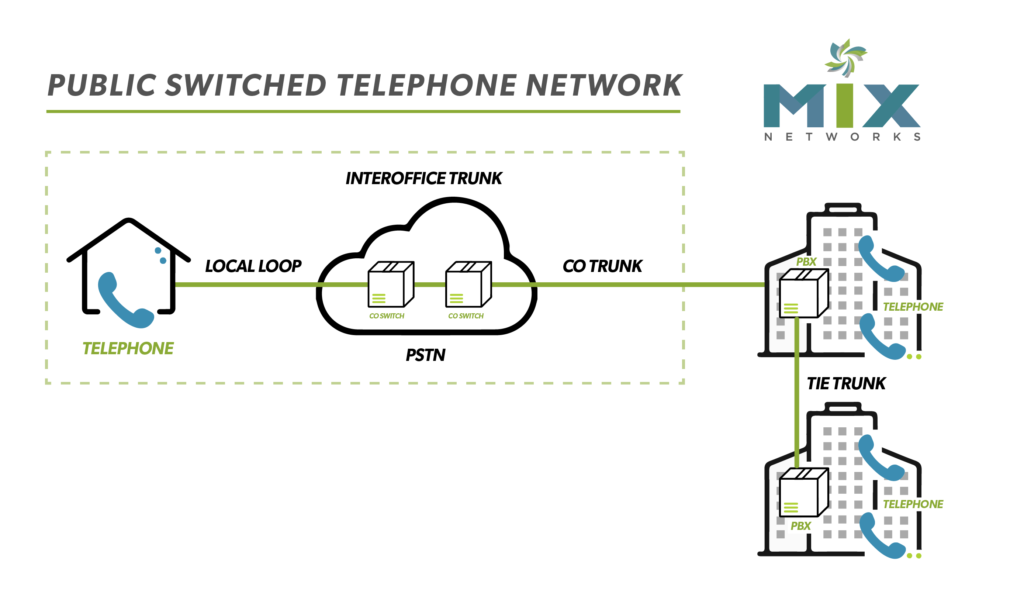
You’ve likely seen the acronym tossed around but do you know what the PSTN stands for?
The PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) was originally designed for voice communications only. Then the PSTN became the underpinning of text messages, video calls, and even the Internet. Using underground copper wires, this legacy platform has been a reliable means to communicate across generations.
Now, the original lines of communications that built the PSTN networks, known as POTS (Plain old telephone service) comprised of twisted copper wires are being replaced by fiber optic cables and data lines. What will happen to this vital network once POTS lines are fully phased out?
PSTN Telephone System Basics
To start, we need to look at the makeup of the PSTN. Comprised of a combination of networks that include POTS Lines as well as fiber optic cables, cellular networks, satellites, and cable systems, the PSTN facilitates communications across borders. To get from one point to the other, the Public Switched Telephone Network is made up of switches that function as nodes. After a call is placed, it is routed through several switches to reach the intended destination and transmit voice signals.*
Additionally, in the United States, the PSTN is made up of local exchange carriers (LECs), regional Bell operating companies (RBOCs), and IXCs (Interexchange Carrier). LECs and RBOCs provide local services such as connecting customers with landline phones and providing directory assistance. IXCs provide long-distance services such as connecting LECs. These entities manage and maintain the nodes, wires, and other equipment needed to maintain the entirety of the network.
The POTS lines within the network also carried ISDN traffic that originally connected computers to the internet, which as we all know, is now obsolete due to the adoption of digital methods of data transfer.
POTS Line Replacement Options
The PSTN is comprised of both POTS lines and fiber optic cables, so as POTS lines are retired, the PSTN will live on. But if you still communicate primarily on the copper POTS lines, you will need to consider how you will communicate once your POTS lines are retired. Thankfully, technology has come a long way and key challenges for businesses with using VoIP and some of our legacy technological needs have been resolved. Fax and alarm solutions have traditionally not worked reliably over VoIP but thanks to POTS Replacement devices, like the POTS IN A BOX© by DataRemote, these challenges are overcome.
Don’t wait any longer – explore your options with POTS IN A BOX© replacement devices or even consider a full rip and replace. The choice is yours – and we can help regardless of which way you choose to go.
Keep Reading:
Why are Businesses Hanging onto POTS Lines?
What is the Difference Between POTS and VoIP?
Why is the PSTN as we know it dying?
Work Cited
*Rosencrance, Linda. “What is PSTN? Definition from SearchNetworking.” TechTarget, https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/PSTN. Accessed 4 October 2022.